Summaries
BHK-21 cells are recommended by the World Health Organization for the production of veterinary vaccines and are widely used for the proliferation of a variety of viruses. Suspension culture of these cells has a history of more than half a century, and nowadays it has become the most common means of producing foot-and-mouth disease vaccine.However, the widely used production process is far from meeting the market demand. Optimizing the production process and improving the production efficiency are the current research hotspots for the scale production of foot-and-mouth disease vaccine reactors. Cell suspension domestication, personalized medium development, and reactor vaccine production and purification process are the key links, this study carried out experiments for the above key technologies, and laid the foundation for the establishment of an efficient production process.
Preamble
Foot and mouth disease (FMD) is an acute, febrile and highly contactable infectious disease caused by foot and mouth disease virus infection, which is mainly susceptible to even-toed hoofed animals. BHK-21 cells, i.e. Baby Hamster Kidney cells, have been widely used for the proliferation of various viruses and the production of veterinary vaccines. The cells are easy to domesticate into suspension culture, which is convenient for large-scale expansion and yield enhancement. The cell is also an ideal host for FMD virus, which can maintain the stable expansion of the virus. As a class A animal infectious disease, foot-and-mouth disease will have a huge impact on the national economy in the event of an outbreak, and vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the disease. With the application of BHK-21 cell suspension production process, the domestic production of FMD vaccine has made great progress. However, the current situation of prevention and control in China is still severe, and the existing production level still has a series of problems such as the need to add serum, cumbersome process, low virus yield and yield, which is far from meeting the market demand. Continuously optimizing the production process and improving the production efficiency are still the urgent demands of the relevant vaccine manufacturers, and the research on efficient FMD production process has great economic value and broad market prospects.
Experimental design
Firstly, a strain of BHK-21 cells sensitive to foot-and-mouth disease virus was suspended and domesticated using B301, a serum-free medium developed by our company. Secondly, the virus production process was initially established by optimizing the conditions of the O-type MYA98 strain, such as the method of catching the virus, the time of harvesting the virus, and the proportion of catching the virus, using a single-variable-control method with the virus 146S as the judgment index. Finally, the virus harvesting and purification process was optimized, and the purification additives were independently developed and screened to improve the virus recovery rate.
Event
Results of serum-free suspension domestication of BHK-21 cells
BHK-21 cells in adherent culture, trypsin-digested and resuspended with B301 medium containing 2% serum, were inoculated in shake flasks at a density of 1×106 cells/mL, and passaged every 48 h. After the cells grew stably, the serum content was gradually reduced until serum-free culture. The results were shown in Figure 1A, and the cells grew stably in successive passages. The fully domesticated cells were inoculated in shake flasks and 10L reactors at a density of 1×106 cells/mL for batch culture, respectively, and the maximum cell density could reach more than 8×106 cells/mL, and the density in the reactor was slightly higher than that in shake flasks (Figure 1B).

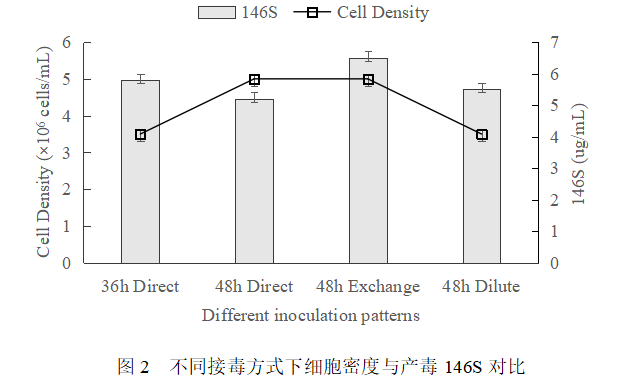
Comparison results of different ways to connect to the poison
The virus was inoculated directly at 36h and 48h after cell inoculation, respectively, while the virus was inoculated after fluid exchange and dilution at 48h after cell inoculation, and the comparison of virus production 146S is shown in Figure 2. Considering the effects of medium nutrient supply, cell growth status and metabolic by-products on virus production, the results showed that the highest virus production was achieved by 48h fluid exchange and virus inoculation, but the enhancement was limited compared with 36h direct virus inoculation. Considering the cumbersome process of fluid exchange operation in large-scale production, which was time-consuming and energy-consuming, the direct virus inoculation was adopted in 36h, which was a cost-saving method.
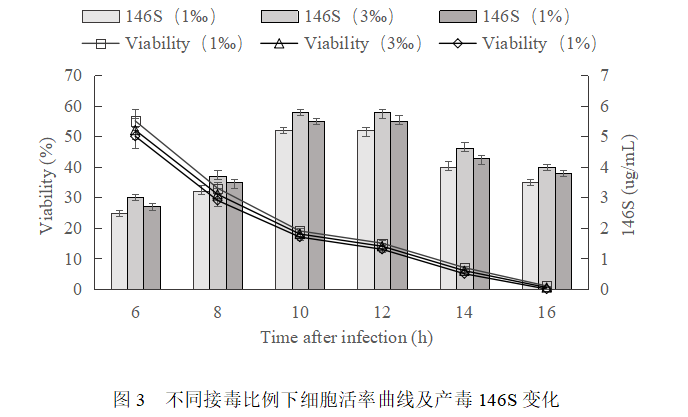
Optimization results of inoculation ratio and collection time
Cell growth 36h to a density of 3.5×106 cells/mL, respectively, according to 1‰, 3‰ and 1% of the proportion of virus inoculation, after inoculation of cell viability and production of 146S change rule is basically the same (Fig. 3), are in the inoculation of 10h-12h, 80%-90% of the cell lesion death of the highest production of 146S, which is the best proportion of the 3 ‰ of inoculation of the virus, 146S up to 6 ug /mL.
Optimization results of purification aid screening
The purification aids PFA, PFB and the combination of the two were added to the harvested viral solution, respectively, and a blank control was set up without the addition of purification aids. After the action, the recoveries were detected by centrifugation, deep filtration and 10-fold concentration on a hollow fiber column, and the recovery of 146S was calculated, and the results are shown in Fig. 4. The combination of PFA and PFB had the highest recovery of more than 90%, which was nearly doubled compared with the blank control.
Summarize
Suspension culture of BHK-21 cells for the production of foot-and-mouth disease virus vaccine is currently the mainstream technology used by domestic and foreign manufacturers of foot-and-mouth disease, however, most domestic enterprises use low-serum culture of cells, when the cells grow to the appropriate density of part of the liquid change into serum-free medium and catch the virus of the production method, the process is cumbersome, low yield, and cause unnecessary waste of medium and energy consumption, which inadvertently increase the cost of production. This process is cumbersome and has low yield, and causes unnecessary waste of medium and energy consumption, which invariably increases the production cost. Optimizing and improving the existing production process to increase the yield and reduce the cost is the urgent demand of the manufacturers.
Cell suspension domestication and serum-free culture have always been the difficulties in animal vaccine production, which require long-term technical accumulation. Thanks to our complete cell domestication and medium development platform and the accumulation of previous practice, we successfully domesticated a strain of BHK-21 cells sensitive to FMD virus into serum-free suspension culture in this study. The cells achieved a stable 1:5 passaging every 48 h of culture, which can meet the demand for expanded production.
The process of virus production determines whether the cell line and culture medium can maximize its potential, and an efficient virus production process can often achieve twice the result with half the effort. In this study, we optimized the virus production process of this BHK-21 cell line using virus 146S as a judgment index. Due to the characteristics of this BHK-21 cell line and the advantages of serum-free culture, the cells have higher energy utilization efficiency during the growth process and fewer metabolic by-products, so there is no need to change or replenish the liquid when inoculating the virus, and the virus can be inoculated directly, which greatly simplifies the production process and improves the production efficiency. After optimization, the best inoculation method was 36h after cell inoculation, the cell density was about 3.5×106 cells/mL, the inoculation ratio was 3‰, and the collection time was 10-12h after inoculation.
The harvesting and purification of virus is also a key link in the production of FMD vaccine. Because the virus harvest liquid contains a large number of cellular debris, nucleic acids and heteroproteins, etc., if it is directly prepared into vaccine without purification and removal of impurities, it is easy to cause a series of adverse reactions when injected into the animal body. The instability of FMD virus makes it easy to be cleaved and inactivated in the process, which also increases the difficulty of harvesting and purification. In this study, two purification reagents were screened and applied in combination, which significantly reduced the loss of virus during centrifugation, filtration and concentration, and nearly doubled the recovery rate, which saved the production cost and improved the production efficiency.






