summaries
Chicken liver cancer cells (LMH cells) were cultured in suspension passages for multiple generations using the personalized medium developed by our company to investigate the stability of cell growth and FAdV-4 amplification. The effects of process parameters such as the multiplicity of viral infections (MOI) and the dilution ratio of the culture medium on the viral potency were further examined by using a one-way experimental method. The production process of FAdV-4 expansion by LMH cell suspension culture was established, which is easy to operate and scale up, and lays the foundation for replacing the current roller bottle production process of FAdV-4C vaccine into a large-scale reactor production process.
preamble
Group Ⅰ avian adenovirus is distributed worldwide, and poultry of all ages are susceptible to it, and the incidence rate is high in China's chicken flocks, with epidemics throughout the country, and the trend is increasing year by year after 2010. The host range of Group I avian adenoviruses is getting wider and wider, white feather broilers, broiler breeders, laying hens and yellow feather chickens can be infected with FAdV-4C, which belongs to Group I avian adenoviruses, and it can cause pericardial hydropericardial hepatitis syndrome (HHS), which leads to the decline of egg production and even death (mortality rate of 20%~80%). The main pathological changes are yellowish clear fluid in the pericardial cavity, enlarged and pale liver, enlarged kidneys, multiple focal necrosis of the heart and liver, and intranuclear inclusion bodies seen in hepatocytes.FAdV-4C has the strongest pathogenicity to chicks, and it can be transmitted horizontally and vertically by contact, which has caused serious economic losses to China's chicken rearing industry.
LMH cells (chicken liver carcinoma cells) are highly sensitive to avian adenovirus viruses, making them one of the best hosts for adenovirus vaccine production. In China, LMH cell culture is based on adherent wall cell culture, which is cumbersome and requires the use of a high proportion of imported serum, with high cost and unstable batch-to-batch quality. Even serum-free suspension culture process is more advantageous. However, the transmission stability of suspended LMH cells for vaccine production has not yet been explored, and the virus production capacity of LMH cells after suspension adaptation and the corresponding process also require detailed experimental studies.
In this paper, a high yielding strain of LMH suspension cell line was used as the starting cell line, and the self-developed medium was applied to its passaging culture for 8 months to investigate the stability of its growth in suspension culture, and to establish the process of virus group I avian adenovirus amplification in shake flasks.
Materials and methods
Experimental design
Suspended LMH cells with no abnormal growth were diluted and passaged every three days (72h) according to the inoculum density of 1.0~1.2×10⁶ cells/ml and cultured in a shaker at 37℃, and the stability of cell growth was examined in the successive passages. The inoculation process was established in shake flasks and process parameters such as MOI and dilution ratio were optimized.
Results
01
Cell Stability Continuous Culture
Shake flasks were continuously passaged for a total of 240 days, the cell morphology was well maintained, the surface was smooth and rounded, all of them were spherical with uniform size, slightly agglomerated, and the cell density of 72h of each generation could reach 5.0~7.0×10⁶ cells/ml, which indicated that the stability of the passaging culture of this culture system was better, and the state of the cell culture was shown in Fig. 1, and the growth curve of the cells after more than 200 days of passaging was shown in Fig. 2.
Figure 1 Diagram of cell status at 72h of culture
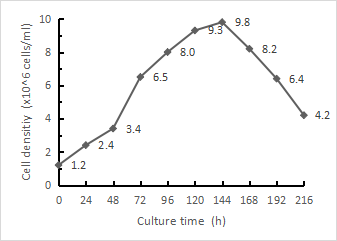
Figure 2 LMH cell growth and proliferation table
02
Establishment and Optimization of Shake Flask Detoxification Process
MOI
Inoculation density 1.0~1.2×10⁶ cells/ml culture 72h dilution inoculation, placed in 37 ℃ shaker culture, the same dilution ratio (i.e. inoculation density) inoculation with different MOI, every 24h sampling and counting observation, retained samples to detect the TCID₅₀ / ml potency, the results show that (Fig. 3). the lower the MOI, the higher the highest inoculation of the virus to achieve the TCID₅₀ The lower the MOI, the later the maximum TCID₅₀max appeared after virus inoculation; on the contrary, the higher the MOI, the earlier the TCID50max appeared.When the MOI was 0.5 and 1.0, the HAmax was higher in 72~96h of inoculation, among which, basically, it could reach more than 9.0lgTCID₅₀/ml in the experimental group, and the highest reached 9.5lgTCID₅₀/ml.
Figure 3 Proliferation effect of FAdV-4 in LMH cells at different MOIs
03
pick-up density
The inoculum density of 1.0~1.2×10⁶ cells/ml was cultured for 72h dilution and inoculation, placed in 37℃ shaker, inoculated with different inoculum densities (i.e., dilution ratios) under the same MOI=1.0, and sampling and counting were carried out for observation and retained samples were tested for TCID₅₀ every 24h, and the results were shown (Fig. 4). The lower the inoculation density, the earlier the highest TCID₅₀ potency (TCID₅₀max) could be achieved after virus inoculation, on the contrary, the higher the inoculation density, the later the TCID50max appeared, in which the experimental group basically could reach more than 9.0lgTCID₅₀/ml, and the highest reached 9.33lgTCID₅₀/ml.
Fig. 4 Proliferation of FAdV-4 in LMH cells at different inoculation densities
Discussion of results
This study shows that the LMH suspension cells domesticated in our laboratory in the matching personalized medium cumulative passaging culture for 240 days is good, its passaging culture is stable, and the cell morphology of the cells in each generation is good, the surface is smooth and rounded, and the cell count at 72h can reach 5.0~7.0×10⁶ cells/ml; at the same time, in the optimal conditions of inoculation of venom (i.e., the optimal inoculation ratio or MOI), the At the same time, under the optimal inoculation conditions (i.e., optimal inoculation ratio or MOI), the highest potency of inoculated adherent culture prepared seed poison (potency of 7.8~8.3lgTCID₅₀/ml) was 9.50lgTCID₅₀/mL, and the suspension culture system established in this study has been initially practically proved in the scale-up of suspension culture production in pilot reactor, which has provided the technical ideas and support for the subsequent large-scale batch production.






